What is labiaplasty?
Labia minora reduction labiaplasty, also known as nymphoplasty, is a surgery in which the excess tissue of the labia minora of the vulva is removed when the lips are hypertrophic or enlarged.
The aim is to offer a harmonious appearance of the vulva and treat any possible discomfort caused by large vulva lips.
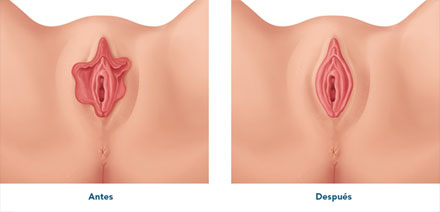
Reasons for undergoing reduction labiaplasty
Considering the existing range of classifications of the labia minora, consensus appears to be greatest in defining hypertrophy of the lips as a lip dimension of over 2 cm measured along its transverse axis. However, lip hypertrophy is not what makes surgery necessary but the desire of the patient to have a more harmonious vulva, and particularly in compliance with her own personal preferences.
It is impossible to define normality when speaking of aesthetic issues, and the ideal beauty concept is conditioned to culture and the times.
The aesthetic aspect is more than enough reason for undergoing reduction labiaplasty.
However, women with large labia minora usually also have a series of other associated symptoms that greatly influence the decision, such as discomfort during exercise, or dryness or irritation caused by friction with underwear when the labia minora are exposed external to the labia majora.
Many women complain of discomfort when trying to insert a tampon or menstrual cup, or during sexual intercourse, when the labia minora invaginate "into the vagina", causing pain due to traction, and embarrassment.
In some cases, the problem may reach the point where the patient avoids wearing tight clothing or bathing suits.
The surgical technique
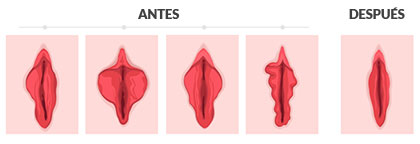
Different surgical techniques are available for correcting the labia minora, involving variable degrees of difficulty and used for different cases and with different aims.
The most widely used procedure is the linear or Trim technique, but there are also other options such as the Wedge or V-technique of Alter or Muñoz, de-epithelization, or resection with the CO2 surgical laser. Other less frequent techniques include Z-plasty or the oval technique.
- Linear (Trim) technique: this is the most widely used procedure and involves elimination of the most external part of the labia minora through a longitudinal cut, sealing the margins with reabsorbable suture. The advantages of the technique are its simplicity, the fact that it is applicable to labia of any size, the absence of tension which helps the healing process and reduces the risk of dehiscences, and the elimination of the most hyperchromic (darkest) portion of the labia.
- Wedge or V-technique: this procedure involves a wedge-shaped incision that can be made at different heights of the labia minora, followed by joining of the margins with reabsorbable suture. This technique is more complex than the linear approach and might not be a good option in the case of very large labia; the suture is subject to tension that facilitates dehiscences, the dark part of the labia is not eliminated, and a scar is left in a less anatomical zone than with the linear technique, thus making it more visible.
- Oval technique: the central portion of the labia is eliminated, followed by joining with reabsorbable suture. The advantages and disadvantages are similar to those of the V-technique.
- Z-plasty technique: the incisions are made in serrate form, followed by closure of the tissue confronting the different edges. This procedure is more often used by plastic surgeons and affords results remarkably similar to those of the linear technique.
- De-epithelization technique: choosing any of the aforementioned incisions, only the epithelial layer is eliminated, leaving the subdermal tissue intact, thereby preserving the erectile and sensory functions of the labia.
- Labiaplasty with the CO2 surgical laser (laser labiaplasty): the difference here is that the incisions are made with the laser, offering the advantage of less bleeding, a lesser need for suture stitches, and faster healing.
There are different anatomical classifications of the labia according to their size along different axes, total or partial lip involvement, whether the presentation is unilateral or bilateral, and aspects such as colour, thickness and symmetry.
Not only lip involvement must be considered but also the anatomical variants of the parallel folds ascending towards the clitoral hood.
The age and hormonal condition of the patient must be considered, since differences in the postoperative course may also cause us to vary the surgery performed.
We therefore must adapt the surgical technique to the existing anatomical situation, but above all to the anatomical form desired by the patient.
It is therefore essential to plan surgery with the patient, explaining the different surgical options in order to afford what she wants. We must offer the possibility of margin preservation or not, explain the possible changes in colour and sensitivity associated with the different techniques, and show the patient in one way or other how things will approximately look like after surgery.
Labia majora filling as a non-surgical alternative to labiaplasty
In patients with mild hypertrophy of the labia minora and doubts as to whether or not to undergo reduction labiaplasty, labia majora augmentation through hyaluronic acid infiltration constitutes an alternative.
Volume augmentation of the labia majora leaves the labia minora a little less visible, affording an aesthetic outcome that is often sufficient for the patient.
The fact that the procedure is reversible defines augmentation as an ideal option when there are doubts in this regard.
Hyaluronic acid infiltration of the labia majora is a simple technique that is performed in the clinic in 30-40 minutes. It involves local anaesthesia and is therefore totally painless and proves very satisfactory for the patient.
Important considerations referred to labiaplasty
Avoid excessive resection
We do not recommend excessive tissue resection, as it may produce a scantly anatomical outcome to the point of constituting a mutilation and can moreover have a non-aesthetic effect with loss of functionality and sensitivity of the labia minora. Small or atrophic labia leave the vaginal introitus (vaginal entrance) more exposed and unprotected, with the risk of dryness and infections.
Assess the need for associated surgeries
In many cases, labiaplasty must be accompanied by other more complex surgeries such as remodelling of the clitoral hood, vaginoplasty and/or perineoplasty, hymenoplasty or reduction of the pubic mound (in cases of a bulgy pubis), in order to correct the possible patient alterations.
Pay special attention to the need for clitoral hood surgery
It is especially important to evaluate the clitoral hood, which requires correction in many surgeries.
Failure to do so results in relative hypertrophy and a poor aesthetic outcome with a virilized appearance due to a more voluminous clitoral hood than before the treatment. This is because it previously went unnoticed because of the presence of the large labia minora.
In sum, poor surgery can have very negative consequences that prove difficult or even impossible to solve afterwards.
Other intimate female surgeries
Clitoral hood reduction
Clitoral hood reduction surgery must accompany most labiaplasty surgeries of the labia minora.
Clitoral hood reduction or hoodplasty involves elimination of the redundant skin covering the clitoris in excess. Clitoral hood reduction or hoodplasty involves elimination of the redundant skin covering the clitoris in excess.

When is it done?
Clitoral hood reduction is usually done and should be done as a complement to reduction labiaplasty of the labia minora, since remodelling of the hood largely tightens and harmonizes the enlarged labia minora.
As isolated surgery, clitoral hood reduction is performed in the presence of a large hood without any other vulvar disorders.
It is increasingly necessary to perform clitoral hood reduction in reparatory intimate surgeries following incomplete or deficiently performed labiaplasties that have had a clearly poor aesthetic outcome.
The clitoral hood: the great forgotten element
The important thing in vulvar surgery is not to forget the clitoral hood.
Reduction labiaplasty without considering the size of the clitoral hood may leave a relatively hypertrophic hood with an anti-aesthetic virilized effect.
This is because when prior to surgery everything was large, surgical reduction only of the labia minora and not the clitoral hood will cause the latter to suddenly seem large, bulgy and with a male visual sensation.
The surgical technique
The usual technique in surgery of this kind consists of de-epithelization of the excess portion of skin, after selecting the size and shape offering the best harmony with the shape of the vulva.
Central reduction may be performed, or two lateral reductions can be decided, continuing with the incision of the labia minora, the anatomical variants, or on an independent basis.
We can use conventional surgery or the CO2 laser, though the latter should be chosen whenever possible because it causes less bleeding and requires fewer suture stitches.
The surgery is simple and sometimes can be performed in the clinic and under local anaesthesia.
Postoperative period
Clitoral hood surgery does not increase the risks or postoperative care of reduction labiaplasty. A relative rest period of approximately 24 or 48 hours is normally advised, with a one-month wait until resuming sports and sexual activities.
Vaginoplasty
Vaginoplasty or vaginal plasty is vaginal reconstruction surgery performed when the vagina has been anatomically affected by tearing, scars such as episiotomy after delivery, or prolapse of the anterior (cystocele) or posterior wall (rectocele).
In cases of mild or moderate vaginal prolapse, the treatment consists of the vaginal CO2 laser. However, if the prolapse is allowed to evolve and become more severe, the solution will have to be surgical.
Correction of a cystocele with reconstruction of the anterior vaginal wall is called anterior vaginal plasty, while correction of a rectocele with reconstruction of the posterior vaginal wall is referred to as posterior vaginal plasty.
In one same surgery it is possible to perform only one plasty or both, depending on the existing anatomical and functional problem.
What tells us who has the problem?
Apart from a clear aesthetic problem with an enlarged vaginal opening, prolapses and/or scarring, patients with these situations suffer functional disorders such as urinary incontinence or urinary retention, constipation and defecation difficulties. In addition, they often experience sexual dysfunction due to reduced contact during coitus or vaginal hyperlaxity.
All these problems can be corrected with the vaginal laser, provided they are not allowed to progress to severe grades.
What does surgery do?
This surgery corrects prolapse (if any) and reduces the vaginal canal lumen, especially at the entrance to the vagina (introitoplasty).
This solves the aesthetic problem and normally also the functional problem.
Since the operated tissue becomes more fibrous and harder, it is advisable to complete the process with some vaginal laser sessions and/or plasma rich in growth factors, in order to improve the tissue, regenerating it and affording elasticity.
Frequently asked questions
Related treatments
Láser CO2 Vaginal
CO2 laser is the treatment that provides the most effective results in regenerative, functional and aesthetic gynecology.
The benefits and applications are innumerable, for example: vaginal dryness and/or atrophy, urinary incontinence, removal of genital warts or treatment of repeated vaginal infections.

Hymenoplasty
The objective is to restore the hymenal membrane so that during the next coitus it can break again and produce bleeding.
There are different surgical techniques to reconstruct the hymen, both conventional and CO2 laser surgery.
Artemédica, aesthetic, functional and regenerative gynecology center in Murcia.
The objective of this medical discipline is to improve the health, quality of sexual life as well as the aesthetics of the female intimate areas.




